Ai Innovation Orca And Progressive learning
AI Innovation: Orca and Progressive Learning
Recent efforts have focused on creating smaller AI models by imitating large foundation models (LFMs). However, issues such as limited imitation signals and homogeneous training data have proven to be challenging. Orca, an innovative model developed by Microsoft Research, was developed to overcome these obstacles using a progressive learning approach.
Overcoming Imitation Learning Challenges
Small AI models often struggle to mimic the reasoning process of LFMs, leading to an overemphasis on the IR capabilities. The emergence of Orca, a 13-billion parameter model, aims to address these shortcomings by learning from the reasoning process of LFMs, with ChatGPT facilitating its learning.
Orca’s Revolutionary Learning Strategy
Orca’s distinctive feature is its progressive learning approach, which enhances learning by using large-scale and diverse imitation data with targeted sampling and selection. This strategy was informed by teacher assistance from ChatGPT.
The Impressive Track Record of Orca
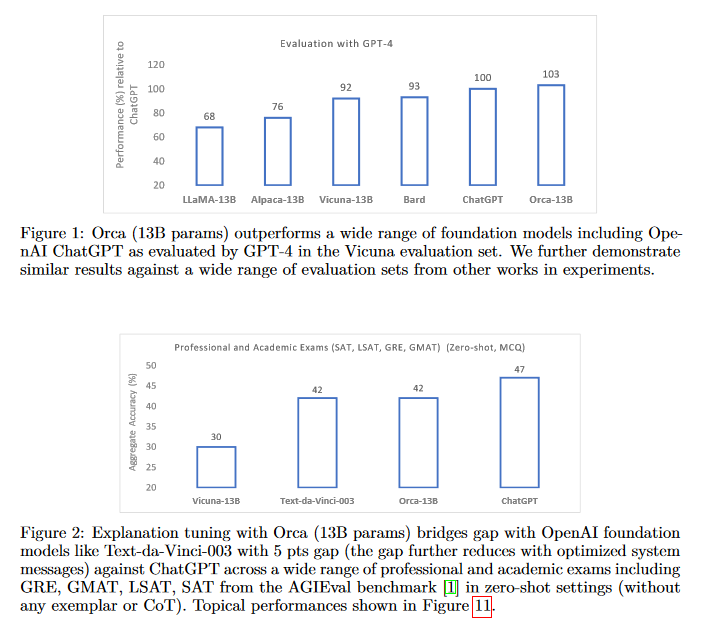
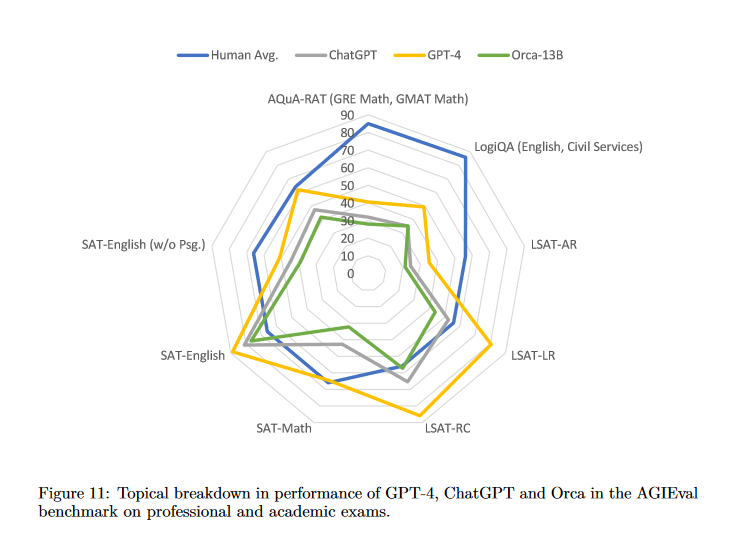
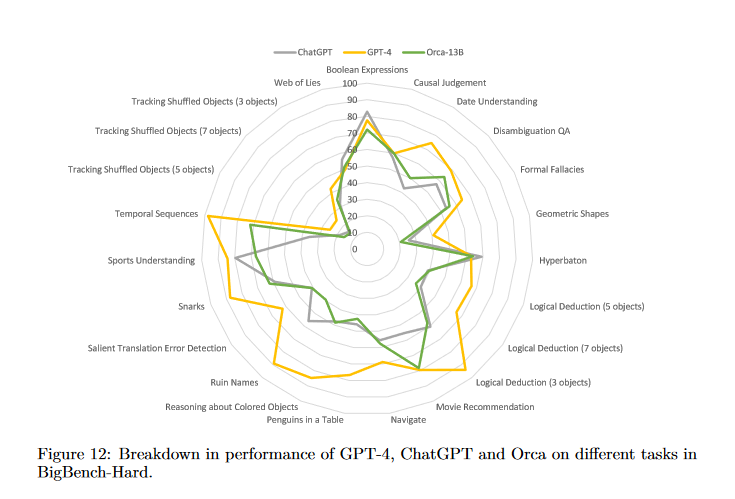
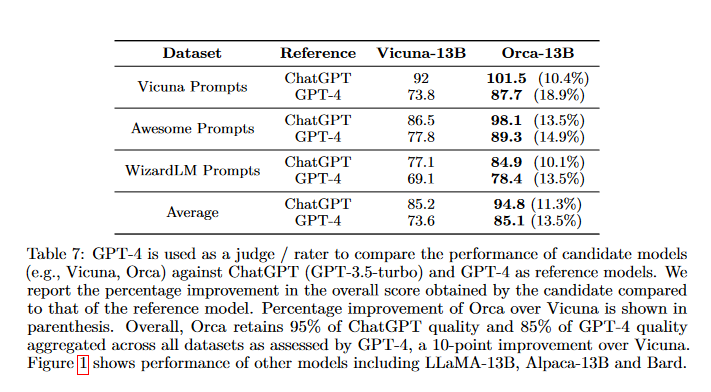
Orca outperformed many established models, doubling the performance of Vicuna-13B in zero-shot reasoning benchmarks such as Big-Bench Hard (BBH) and improved AGIEval by 42%. It also showed comparable performance to ChatGPT on the BBH benchmark and performed well in professional and academic examinations.
The Future of AI Learning with Orca
The progressive learning approach used by Orca signals a new era of AI advancement. AI models can supervise their behavior or that of other models, thereby optimizing their performance. Orca’s success shows promise for further research on leveraging LFMs’ reasoning process to create even more capable AI models.
LFMs: Powerhouses of AI
LFMs such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 have shown impressive performances across a range of tasks owing to the scaling of the model and dataset sizes and the introduction of a second training layer to align the models with user intent. Smaller models are increasingly using these LFMs as teachers to generate large datasets, instruct, and train.
Understanding the Challenges of AI Learning
While smaller models can imitate LFMs’ style, they often lack the reasoning skills of their larger counterparts. Instruction-tuning research mimicking LFMs has limitations, including simplistic instructions, task diversity issues, limited imitation signals, and evaluation challenges.
Orca’s Performance: Setting a New Standard
Orca has proven its prowess by achieving parity with ChatGPT on complex tasks and significantly outperforming Vicuna, a prominent 13-billion parameter instruction-tuned model. The gaps between these models highlight the need for strategies to improve reasoning and comprehension.
Solutions Proposed by Orca
Orca addresses these challenges through explanation tuning, which includes detailed GPT-4 responses that explain the reasoning process and scaling tasks and instructions using the Flan 2022 Collection, creating a diverse training set. Orca’s success offers promising avenues for the development of more powerful AI models.
Evaluating Orca’s Capabilities
The functionality of ChatGPT as a teaching assistant was tested through rigorous evaluations of Orca. The assessments encompassed the following:
- AutoEvaluation with GPT-4: Using Vicuna and WizardLM’s existing evaluation sets, and an extensive prompts collection.
- Academic Assessments: Rigorous academic tests like Big-Bench Hard and TruthfulQA.
- Standardized Exams: They assessed Orca using professional exams like SAT, LSAT, GRE, and GMAT with AGIEval.
- Safety Checks: ToxiGen was used to check Orca for toxic language and hate speech.
Unpacking Instruction Tuning
Instruction tuning allows pre-trained language models to learn from input-response pairs, enhancing their performance on various benchmarks. This technique has been adopted by models such as Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, and Koala to train smaller language models.
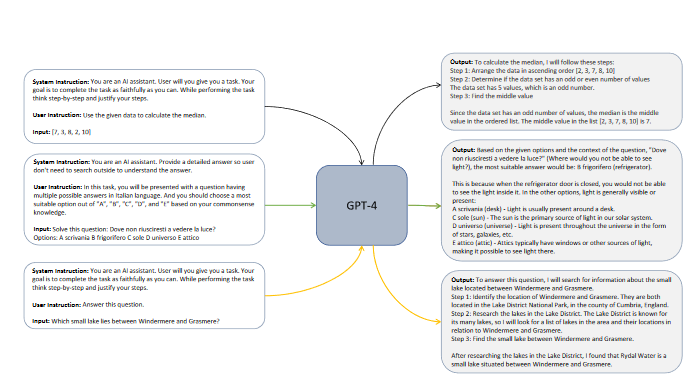
System Instructions: A Guiding Light
System instructions in models such as GPT-4 guide behavior and responses, specifying the tone, task, format, and limitations of responses. They improve the safety of model responses, helping the AI avoid generating harmful content and respecting user privacy.
Pioneering Explanation Tuning
This approach utilizes large-scale training data with diverse tasks, complex instructions, and rich signals to address the limitations of the existing methods.
Dataset Construction
The training data included instances of the system messages, user queries, and responses. System messages provide context, whereas user queries define the model’s task. The FLAN-v2 collection provided user queries and instructions for this experiment, thereby creating a rich dataset. The application of AI in education using models such as ChatGPT as teaching assistants unveils exciting opportunities for progressive learning. Evaluations and techniques indicate that, with correct tuning and instructions, AI can indeed be a valuable educational resource.
System Messages and Performance Analysis
System messages aim to enhance the model’s capabilities by allowing detailed explanations and step-by-step reasoning. The authors created various system messages to generate diverse answers from the AI. The FLAN-v2 collection, a diverse dataset, provided the bulk of the training tasks. Tasks included math problem-solving, natural language inference, and common-sense reasoning. A performance comparison between Orca, ChatGPT, and GPT-4 on tasks involving world knowledge, logical reasoning, and table understanding revealed the strengths and weaknesses of each model. For example, Orca lagged behind in logical reasoning and table understanding but did better in movie recommendation tasks. A safety evaluation focused on Orca’s truthfulness and its tendency towards neutral language and hate speech. The results showed that Orca’s outputs were significantly more truthful than Vicuna-13B, but still trailed behind ChatGPT and GPT-4.
The Journey of Language Models: Size vs Efficiency
With language models growing in size, the aim is to achieve similar capabilities using smaller and more efficient architectures. A performance comparison between smaller models and advanced models, such as ChatGPT and GPT-4, shows a persistent performance gap.
Exploring Explanation Tuning
Explanation Tuning, a method that allows smaller models to align with GPT-4, plays a crucial role in this research. This shows that data size, coverage, and quality are paramount in this alignment process.
Importance of Step-by-step Explanations
This study underscores the significance of learning from step-by-step explanations. These detailed breakdowns, regardless of the model size, greatly enhance the output quality.
Notable Limitations and Future Prospects
Although promising, smaller models come with their own set of challenges. These include potential data biases, lack of real-world understanding, and risk of misuse. In addition, the performance of a model such as Orca is influenced by the data used for explanation tuning and may exhibit limitations in underrepresented areas of the training dataset.
Wrapping Up
The pursuit of smaller and more efficient language models is ongoing. Research with Orca illustrates that achieving remarkable results with smaller models is feasible, especially when coupled with techniques such as Explanation Tuning. However, addressing the performance gap with larger models, such as GPT-4, remains a challenge. These insights aim to stimulate further research and development in the field of AI, pushing the boundaries between what is possible in education and beyond.
Paper:
Orca: Progressive Learning from Complex Explanation Traces of GPT-4 arXiv:2306.02707, Submitted on 5 Jun 2023.